SAP roles are a (two dimensional) table structure; a user has multiple roles, and each role has multiple attributes. The ERP MA considers this to be a complex type, meaning the data cannot be treated as simple value type (i.e. string, number, etc) nor a list of simple types. The ERP MA handles complex types by serializing the entire structure as an Xml string.
Prerequisites to configure the ERP MA to handle roles
- An existing configuration such as
user-export-replace. For more information, see How To Configure a
Replace User Operation.
- A roles attribute have been created in FIM as
type string.
- The role management BAPI have been added to
active configuration.
-
In the configuration file, map the CS attribute directly to the complex function/parameter (i.e. to the structure and not to a field on the structure.) At runtime the ERP MA will then detect that this is not a simple type that can be retrieved in a straight-forward way and serialize the structure to Xml string.
-
You will also need to configure a runtime check condition for the BAPIs used to manage role to ensure that the BAPI's do not run if role data is not supplied and/or if they've not been changed.
-
Below is a sample serialized xml. This sample shows two assigned roles for a user. To see what the exact structure will be for you SAP environment, it's recommended that you first run and import and observe the structure/field-names.
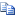 Copy Code
Copy Code<BAPIAGRTable> <BAPIAGR> <AGR_NAME>HR_1</AGR_NAME> <FROM_DAT>20020205</FROM_DAT> <TO_DAT>99991231</TO_DAT> <AGR_TEXT>Employee Self-Service (HR)</AGR_TEXT> <ORG_FLAG/> </BAPIAGR> <BAPIAGR> <AGR_NAME>SAP_EMPLOYEE_1</AGR_NAME> <FROM_DAT>20020301</FROM_DAT> <TO_DAT>99991231</TO_DAT> <AGR_TEXT>Employee Self-Service (LO)</AGR_TEXT> <ORG_FLAG/> </BAPIAGR> </BAPIAGRTable>
 Note
NoteTo consume this xml string, the consumer will need to implement a facility to parse/read/modify this xml string (such as an MV Extension).