The request processing model within Forefront Identity Manager (FIM) is composed of three main phases: authentication, authorization, and action. Workflows (each of which contain one or more activities) can be attached to each of these phases and run in the context of executing a single request. The objective of this section is to provide a more detailed description of how requests are processed in FIM.
Understanding the Request Processing Model
The request processing model in FIM is composed of three main phases:
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Action
Workflows, each of which contains one or more activities, can be attached to each of these phases and run in the context of executing a single request. A request can initiate from a single user call to one of the web service endpoints or through a user creating a request in the FIM Portal.
The following illustration shows the relationship of the request processing components:
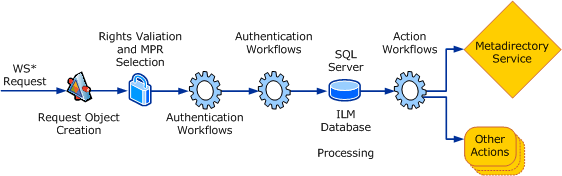
Processing requests
Requests are processed in the following order:
- Request Object Creation- FIM creates a Request object in
response to a call to one of the web service endpoints or because
of a request initiated through the FIM Portal.
- MPR Evaluation - The requester’s rights to request the
action are validated and the computation of the applicable
workflows is performed. The request is checked against mappings to
any MPR objects. To map to an MPR, all the applicable fields of the
MPR for the requested operation need to match. This includes the
requester, operation, target resource, and attributes. If all of
these conditions including the attributes being affected are true
for an incoming request, then the appropriate MPR is matched to the
request. A request must map to at least one MPR that grants the
permission as part of its definition. If this is true, the request
passes through the permissions check stage of request processing.
If this is not true, the request fails. The system also determines
the set transitions that are part of the request and locates all
related set transition-based MPRs.
- Authentication - FIM runs authentication workflows one
at a time in a nondeterministic order to confirm the requester’s
identity.
- Authorization - FIM confirms the requester’s permission
to perform the requested operation on the resource specified in the
request. All dependent authorization workflows are run in parallel,
but a request is not committed to the FIM Object Store unless all
of the workflows have been completed and all have succeeded.
- Processing - FIM performs the requested operation on the
FIM Application Store.
- Action - FIM executes any processes that are to occur
because of the requested operation. All action workflows are run in
parallel. Read operations do not have any workflows applied to
their processing. This includes the configured workflows in the
RMPR as well as the workflows in the set transition-based MPRs.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Requests initiated by the Synchronization Account bypass all authentication and authorization workflows that would be applicable to them. Any applicable action workflows are applied. |
Related Resources
- The Request resource
stores information about a request.
- The approval activities released with FIM use
the Approval
and ApprovalResponse
resources to store information about approvals. Those objects are
managed by the approval activity and can be accessed by custom
activities or other internal components.
- The WorkflowDefinition
resource is used to store the workflow definitions that can be
associated with a request.
- The WorkflowInstance
resource stores details about a specific instance of a workflow
that is running.