When processed by GateWall Antispam, messages go through several filtering stages, including connection filtering, sender filtering, recipient filtering and content filtering. At the last stage, a message is filtered in accordance with the rules created by the administrator.
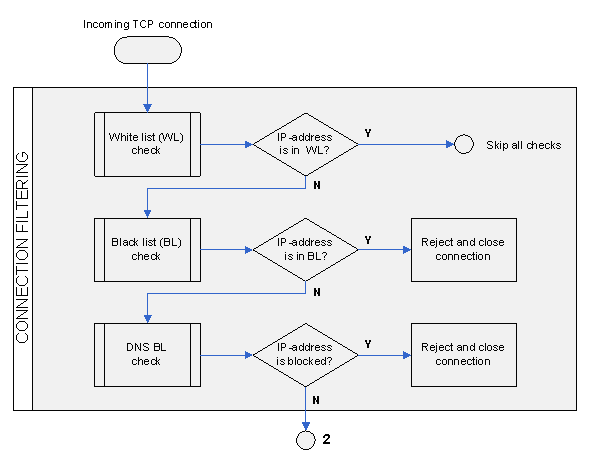
Connection filtering flow chart is shown in Fig. 1. When an incoming connection is registered on TCP port 25, GateWall Antispam server scans through its global white list of IP addresses. The white list is assigned on the "Antispam - Black and White Lists" page. Each list item may be an IP address (a range of IP addresses), a domain name (A-type record) or a name of domain mail exchanger (MX-type record). GateWall Antispam server resolves the listed names into corresponding IP addresses and generates global lists of resolved and restricted IP addresses. If the incoming connection originates from a white list IP address, GateWall Antispam will skip all subsequent checks up until the rules created by the administrator and receive the message. GateWall Antispam will block connection for IP addresses listed on the black list.
The next step is DNSBL check. If the incoming connection originates from an IP address that is on the spam list, GateWall Antispam will reject and close the connection and generate a corresponding error message. You can set DNSBL parameters on the corresponding page of the administrator console. DNSBL parameters include names of DNSBL servers used in the check process and the exceptions list. Each exceptions list item may be represented by an IP address, domain name or name of mail exchanger.

Fig. 1. Connection Filtering
If the MAIL FROM command does not contain a blank address, GateWall Antispam server will scan the black and white lists for this address. If the address is found on the black list, GateWall Antispam will close the incoming connection and produce a corresponding error message. If the address is on the white list, all subsequent checks will be skipped.
The next step is to check if the domain whose address is listed in the MAIL FROM command has an MX (Mail eXchanger) record and a SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record. To enable MX record check, go to "Antispam - Key Settings" page of the administrator console. SPF check parameters are assigned in the Antispam section of the corresponding SPF page. You can set GateWall Antispam to respond to the results of MX and SPF checks in the server settings.
The last step is to complete RHSBL filtering by the domain name listed in the MAIL FROM command. If the domain name is found on the spam list, GateWall will close the incoming connection and produce a corresponding error message.
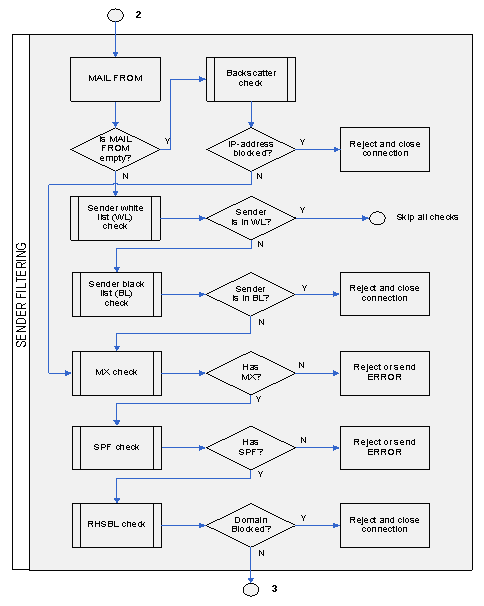
Fig. 2. Sender Filtering
GateWall Antispam starts recipient filtering after the RCPT TO command has been received. The received address is checked against the black and white lists. If the destination address is found in the white list, all subsequent checks will be skipped. If the address is found on the black list, GateWall Antispam will close the incoming connection and produce a corresponding error message.
Next, GateWall Antispam checks the availability of the destination address in accordance with the set routes ("Virtual SMTP Server - Routes" page). To complete the check, GateWall Antispam connects to the mail server specified in the route and requests the vailability of the recipient by sending the RCPT TO command. If the mail server contains no such recipient address, GateWall Antispam will produce a corresponding error message.
For each incoming connection, GateWall Antispam creates a triplet (IP address originating the connection, MAIL FROM address and RCPT TO address) and scans the internal list of triplets for previous connections. If the received triplet is not found in the internal triplet list (i.e. the connection with the given parameters is a new connection), GateWall Antispam will produce a temporary error message. This is a Greylisting check procedure. You can set the Greylisting parameters in the Antispam section of the corresponding Greylisting page.
GateWall Antispam supports the Tarpitting feature to protect you from address matching. The Tarpitting feature "delays" mail server response when a new destination address is received in the RCPT TO command. By default, response delay will be enabled if more than five destination addresses are received at once. You can set the required Tarpitting parameters on the "Antispam - Key Settings" page.
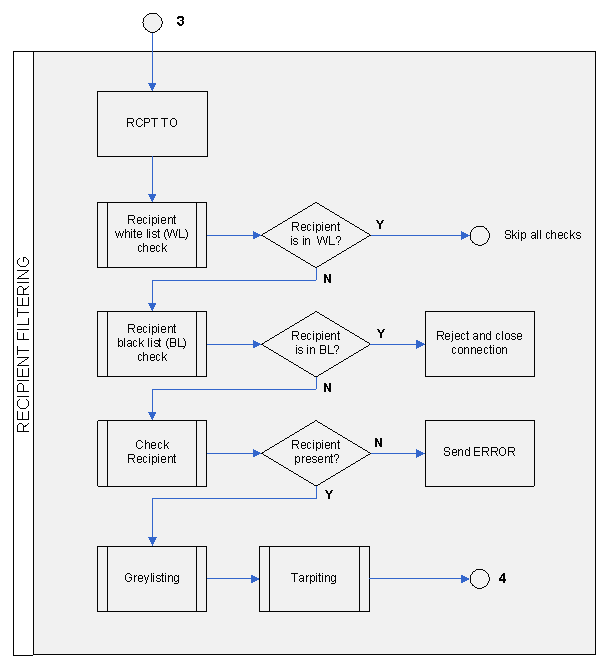
Fig. 3. Recipient Filtering
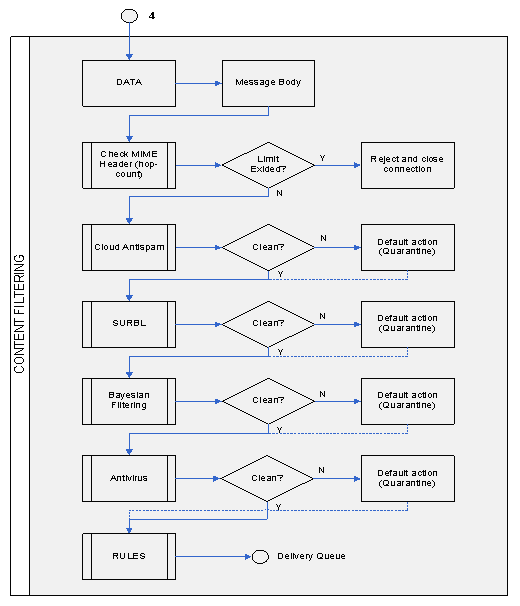
GateWall Antispam will start content filtering after the message body has been received. The first step is to check MIME headers. If the message delivery route specified in the header is longer than the set limit ("Maximum Forwarding Distance" parameter on "Virtual SMTP Server - Settings" page), GateWall Antispam will block the message. Besides, a reply message will be generated at the MIME check step if the Autoreply function is enabled. The next step is to check the entire message using an online service (the so-called Cloud Antispam). The application sends a unique message hash to a remote server using the HTTP POST method. Cloud Antispam requires HTTP to be enabled on the computer where GateWall Antispam is installed. Messages identified as spam or infected messages (Cloud Antispam also scans messages for viruses) are placed into the quarantine folder (%GWA%\mail\quarantine). You can push messages in the quarantine folder to their destination addresses. To do so, move the corresponding *.xeml file of a message from "%GWA%\mail\quarantine" folder to "%GWA%\mail\import" folder. To push-send a message, use the shortcut menu on the "Monitoring" page. Next, GateWall Antispam completes SURBL filtering and statistical check (Bayesian filtering). The Bayesian filtering algorithm designed by Entensys allows automatic learning using the messages identified by Cloud Antispam as "clean messages." The last step includes virus check and message processing using the rules.