This topic describes key technical features of Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG).
Audience
This topic is recommended for anyone who is new to Forefront UAG, including business decision makers, technical experts, security administrators, and Forefront UAG administrators.
Forefront UAG features
The main Forefront UAG deployment scenarios are as follows:
- Application publishing─You can publish
internal corporate applications, including Web applications,
non-Web applications, Remote Desktop Services (RDS) application,
and full VPN access to internal networks. Remote users access the
published applications over HTTP or HTTPS, from a diverse range of
client devices.
- DirectAccess─You can configure
Forefront UAG as a DirectAccess server, to provide a seamless
connection to internal resources for client devices that are
running as DirectAccess clients. Client requests are securely
directed to the internal network, without requiring a VPN
connection. Forefront UAG DirectAccess extends the benefits of
Windows DirectAccess by providing scalability, access to IPv4
resources, and simplified deployment.
A Forefront UAG server can be configured for both application publishing and DirectAccess. The only exception is that you cannot publish the Network Connector application if you have configured DirectAccess.
The following diagram shows a basic topology for Forefront UAG.
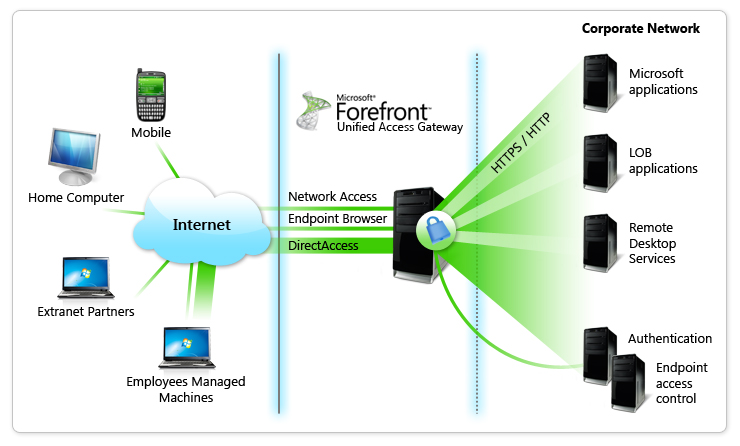
Application publishing
Application publishing consists of the following elements:
Trunks and applications
To allow remote access to internal applications, you create Forefront UAG HTTP or HTTPS trunks, where each trunk is a unique listener (combination of IP address and port). You publish applications by adding them to a trunk. Client devices can access published applications as follows:
- Via a portal─Client devices access the application via
the trunk portal, by typing in the IP address of the trunk.
- Directly─Client devices access Web applications
directly. To do this, you publish Web applications with an
application-specific public host name. Users then type this host
name in the browser, and connect directly to the application
without needing to access the portal.
For each trunk you can configure IP addresses, public host name and ports, authentication requirements, access policies with which client devices must comply, a logoff policy, and a traffic inspection policy. You also configure settings for each application published via a trunk. The exact settings depend on the type of application, but include IP addresses and paths of published servers, access policies for the application, single sign-on (SSO) settings for forwarding trunk credentials to published application servers, access policies, and security settings.
For more information about trunks and applications, see Overview of application publishing.
Client devices
Users connect to a Forefront UAG trunk portal or Web application by typing the portal or application address in a browser. When a client device attempts to connect, Forefront UAG detects whether Forefront UAG client components can be installed on the client device, according to the client prerequisites described in System requirements for Forefront UAG client devices. The following features require the installation of client components:
- Client device detection—Based on the
detection results, client devices are granted or denied access.
- Browser cache cleanup—Forefront UAG can clean
up the browser cache at the end of an access session.
- Non-Web protocol access—There are a number of
components that are required for access to non-Web
applications.
Client components are not required for:
- DirectAccess
- Access to Web applications published via
Forefront UAG
- Access to RDS RemoteApps published via
Forefront UAG.
- Acess to Outlook Anywhere or Exchange
ActiveSync published via Forefront UAG
- User authentication
Forefront UAG provides the following client components:
- Forefront UAG Endpoint Component
Manager—Downloads, installs, manages, and removes all the
Forefront UAG endpoint components. There are two versions of this
component: ActiveX and Java Applet.
- Forefront UAG Endpoint Session
Cleanup—Deletes persistent data that is downloaded for a
Forefront UAG session. There are two versions of this component:
ActiveX and Java Applet.
- Forefront UAG Endpoint
Detection—Assesses whether a client device complies with
Forefront UAG access policies.
- Forefront UAG Client Trace
component—Used for client-side tracing.
- Non-Web tunneling components:
- Forefront UAG SSL Application
Tunneling—Provides SSL connectivity for non-Web protocols.
There are two versions of this component: ActiveX and Java
Applet.
- Forefront UAG Socket Forwarding—Used
to support a wider variety of applications that the Forefront UAG
SSL Application Tunneling component.
- Forefront UAG SSL Network
Tunneling—Used to support remote client VPN connections to the
entire internal corporate network.
- Socket Forwarding Helper—Used for
support purposes.
- Forefront UAG SSL Application
Tunneling—Provides SSL connectivity for non-Web protocols.
There are two versions of this component: ActiveX and Java
Applet.
For more information, see the Client component deployment planning guide.
Access controls
Forefront UAG provides a number of mechanisms to control access to the Forefront UAG portal and published applications, including:
- Client authenticationincluding:
- Session authentication—You can require
users to authenticate in order to access a Forefront UAG session.
Forefront UAG can verify user credentials against a wide variety of
authentication methods, including Active Directory, LDAP, LDAP
client certificates, RADIUS, RSA SecurID, AD FS, TACACS, WINHTTP,
and customized authentication.
- Single sign-on (SSO)—You can configure
SSO settings that forward client credentials provided during
session logon to backend published servers. For SSO Forefront UAG
can perform Kerberos authentication (for applications that support
Kerberos) on behalf of client devices, or users can authenticate
using a 401 request or an HTML form.
- Session authentication—You can require
users to authenticate in order to access a Forefront UAG session.
Forefront UAG can verify user credentials against a wide variety of
authentication methods, including Active Directory, LDAP, LDAP
client certificates, RADIUS, RSA SecurID, AD FS, TACACS, WINHTTP,
and customized authentication.
- Access policies—Forefront UAG can
require client devices to conform with inbuild uagshort access
policies (predefined or custom), or validate client device settings
against Network Access Protection (NAP) policies downloaded from a
Network Policy Server (NPS).
- Portal application authorization—For
each application published via a portal, you can limit access to
the application to specific users and groups only. Authorization is
implemented using users and groups defined on a selected
authentication server.
For more information about access controls, see the Access control for publishing planning guide.
Direct Access
Forefront UAG acting as a DirectAccess server provides the following
- Ease of management—Configure Forefront UAG DirectAccess
using a series of wizards built into the Forefront UAG Management
console.
- Remote management—Deploy Forefront UAG DirectAccess to
manage remote corporate computers that are configured as
DirectAccess clients, and are connected to the Internet. You can
perform management tasks such as group policy changes, and update
distribution, even when users are not logged on.
- Remote access—Deploy Forefront UAG DirectAccess to
provide remote DirectAccess client computers with seamless
connectivity to corporate networks. Using Forefront UAG you can
provide access to both IPv6 and IPv4 resources.
- DirectAccess clients—Configure managed computers as
DirectAccess clients by applying the DirectAccess client GPO to
computers located in a specified security group or OU. Using the
DirectAccess Wizard, you specify a security group or OU in which
DirectAccess client computers are located, and configure the client
GPO.. In addition,
- DirectAccess Connectivity Assistant (DCA)—We recommend
that you deploy the DCA application on DirectAccess client
computers. This application provides information about DirectAccess
connectivity in the Windows taskbar. In the DirectAccess wizard,
you can define DCA settings that will be applied when you deploy
the DCA application.
- Authentication and encryption—Forefront UAG DirectAccess
client computers are authenticated even before the users logs on.
In addition, users are authenticated, and you can add extended
authentication methods, including smart cards and one-time
passwords (OTP). Traffic between DirectAccess clients and the
DirectAccess server is encrypted with IPsec, and you can choose to
extend encryption to traffic between the DirectAccess server and
specified internal servers.
- Force tunneling—Specify how DirectAccess clients access
the Internet. You can require clients to access the Internet via
the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server.
- Client health—Optionally verify the health of
DirectAccess clients against Network Access Protection (NAP)
policies. Policies can be retrieved from an Network Policy Server
(NPS) running on the local Forefront UAG server, or from a remote
NPS.
For more information about Forefront UAG DirectAccess, see the Forefront UAG DirectAccess planning guide.
Single server and array deployment
Forefront UAG can be installed on a single server, or you can deploy an array of multiple Forefront UAG servers for scalability, high availability, and failover. A Forefront UAG server can act as both an application publishing server, and as a DirectAccess server. In an array, each server shares the same configuration, including DirectAccess settings, and trunk settings. One of the array members acts as the array manager, and stores configuration settings for the entire array. You can load balance array traffic using a hardware load balancer, or Windows Network Load Balancing (NLB) integrated into the Forefront UAG Management console. For more information, see the Array planning guide.