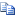
To encourage computers to comply with security and health requirement policies and reduce the risk of malware spreading, non-compliant clients can be restricted from accessing intranet resources or communicating with compliant computers. Using Network Access Protection (NAP) with Forefront UAG DirectAccess, IT administrators can require DirectAccess client computers to be healthy and comply with corporate health requirement policies. For example, client computers can obtain a connection to the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server only if they have recent security updates, anti-malware definitions, and other security settings.
Using NAP in conjunction with Forefront UAG DirectAccess, requires that NAP-enabled DirectAccess clients submit a health certificate for authentication when creating the initial connection with the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server. The health certificate contains the computer’s identity and proof of system health compliance. A NAP-enabled DirectAccess client obtains a health certificate by submitting its health state information, either to a Health Registration Authority (HRA) that is located on the Internet before initiating a connection to a Forefront UAG DirectAccess server, or to an internal HRA server accessible using the infrastructure tunnel.
By using NAP with Forefront UAG DirectAccess, a non-compliant client computer that becomes infected with malware can still connect to all the specified management servers (for example, DNS, DC, HRA, and remediation servers) through the infrastructure tunnel, but it cannot connect to all other intranet resources. Access to the remediation servers using Forefront UAG DirectAccess is crucial to remediate the non-compliant state of the client. NAP is not required to use Forefront UAG DirectAccess, but it is recommended.