Before you deploy Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) 2.0, you should be aware of the supported and unsupported scenarios, and the prerequisites for deploying your system.
Supported scenarios
AD FS 2.0 in Forefront UAG requires the following environment:
- An AD FS 2.0 server.
- The AD FS 2.0 server is defined as
an authentication server in Forefront UAG. When you use an
AD FS 2.0 server for trunk authentication, it must be the
only authentication server. When you use an AD FS 2.0
server for application authentication, it must be the only
authentication server.
- Shadowed accounts are required when the
published application supports the Kerberos version 5 protocol and
you want to provide single sign on (SSO) using Kerberos constrained
delegation.
 Note:
Note:To use Kerberos constrained delegation, Forefront UAG must be domain joined. - You can only publish claims-aware
applications and the AD FS 2.0 application on an HTTPS
trunk.
- You can configure your AD FS 2.0
server to use forms-based authentication; however, Forefront UAG
does not support this configuration by default and cannot perform
SSO to the AD FS 2.0 server. To enable SSO to the
AD FS 2.0 server when you use forms-based authentication,
you must add a customized form login for SSO on the Forefront UAG
server.
- You can use your AD FS 2.0 server
in only one trunk. If you require additional trunks, you must use
additional AD FS 2.0 servers, each with a new public host
name and Federation Service.
When using SSO to claims-aware applications with AD FS 2.0 and Forefront UAG, SSO is performed by the AD FS infrastructure, not by Forefront UAG.
Unsupported scenarios
When using AD FS 2.0 and Forefront UAG, you cannot publish applications that are installed on the AD FS 2.0 server.
You cannot use an HTTP to HTTPS redirection trunk to redirect HTTP requests from end users to your HTTPS trunk.
End users cannot use mobile devices to access trunks that use federated authentication.
You cannot end user sessions from the Forefront UAG Web Monitor. If you do end a user session using Web Monitor, single sign-out does not take place and the end user may receive an HTTP 500 error page.
Topology prerequisites
Before you can deploy AD FS 2.0 and Forefront UAG, make sure that you have the following configured.
For all topologies:
- An Active Directory Domain Services
(AD DS) server in your organization. Active Directory
Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) is not supported by
AD FS 2.0.
- An AD FS 2.0 server in your
organization. You can run AD FS 2.0 on the same server
that you use as the AD DS server. For information about
downloading and installing the AD FS 2.0 software, see
Install the AD FS 2.0 Software
(http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=192792).
- Your AD FS 2.0 server and your
Forefront UAG server must have the same domain name in the
certificates they use for authentication; that is, the public host
name of the AD FS 2.0 server must have the same domain
name as the certificate that you use when creating the HTTPS portal
trunk on Forefront UAG. For example, if you use a wildcard
certificate *.contoso.com, your public AD FS 2.0 server
name can be adfs2.contoso.com, or fed_auth.contoso.com, but not
adfs2.hr.contoso.com.
- The public host name of the
AD FS 2.0 server (defined in Forefront UAG) must be the
same as the Federation Service name (defined in the
AD FS 2.0 management console).
- On each federation server required by the
topology, make sure that the Federation Service identifier is set
to HTTPS.
For topologies providing access to your remote employees:
- Forefront UAG behaves like a “man in the
middle” in AD FS 2.0 deployments. IIS on the
AD FS 2.0 server automatically protects against man in
the middle attacks using a Channel Binding Token (CBT). However, if
the CBT is enabled, you cannot provide access to your remote
employees. To turn off CBT, on the AD FS 2.0 server in
your organization, run the following command:
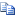 Copy Code
Copy Codeappcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site/ADFS/ls" -section:system.webServer/security/authentication/windowsAuthentication /extendedProtection.tokenChecking:"None" /extendedProtection.flags:"Proxy" /commit:apphost
For topologies providing access to partner employees:
- A federation server in the partner
organization. The partner federation server must support Security
Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 tokens.
- On the federation server in the partner
organization, make sure that your AD FS 2.0 server is
added as a relying party trust. For information, see Create a Relying Party Trust Using Federation Metadata
(http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=192793).
- On your AD FS 2.0 server, in the
AD FS 2.0 management console, make sure that the partner
federation server is added as a trusted claims provider. For
information, see Create a Claims Provider Trust Using Federation
Metadata (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=192794).
General deployment information for your organization:
- Forefront UAG is not required to be a part of
the same domain as the AD FS 2.0 server or the
applications that will be published. However, if you want to
provide single sign-on with Kerberos constrained delegation,
Forefront UAG must be joined to a domain.
- Applications can be published through
Forefront UAG using three types of publishing template:
- External URL-aware applications—Relevant for
applications that are aware of their external URL. For SharePoint
applications, this is referred to as Alternate Access Mapping
(AAM).
- Alternate Publishing Name (APN)—Similar to
external URL-aware applications, but in this case, the application
is not aware of its external URL. When publishing multiple APN
applications, Forefront UAG identifies traffic for each application
based on the host header. Therefore, applications published with
this template use host names with the same domain as the portal,
but with different host headers, for example, if the portal URL is
portal.contoso.com, the application URL might be
app1.contoso.com.
- Host Address Translation (HAT)—When you
publish an application using HAT, its external URL is based on the
portal URL, but the application URL contains a unique signature
that allows Forefront UAG to identify traffic that is intended for
the particular application. For example, if the portal URL is
portal.contoso.com, the application URL might be
portal.contoso.com/portala6bb873kdkj36678/portal1/.
You can publish all application types using HTTP for communication on the internal network, and HTTPS on the external network. However, when you publish HAT and APN applications in this manner, end users cannot access the published application from the internal network: users must access the application through the external address. To publish HAT and APN applications using HTTP for communication on the internal network make sure that:
- The endpoint URL in the application
federation metadata is the external HTTPS address of the
application.
- You have configured the relying party trust
between the application and the AD FS 2.0 server.
- You have edited the web.config file and
within the
<wsFederation>tag, you have typedreply=<externalURI>, where externalURI is the external HTTPS address of the application.
- External URL-aware applications—Relevant for
applications that are aware of their external URL. For SharePoint
applications, this is referred to as Alternate Access Mapping
(AAM).
Client requirements:
- Client computers can be running any supported
Windows operating system (see System requirements for
Forefront UAG client devices) and can use supported Internet
Explorer and Firefox browsers. End users cannot use mobile devices
to access trunks that use federated authentication.
 Important:
Important:The following URLs must all be in the same security zone, for example, by adding all of the URLs to the Trusted Sites list: - Forefront UAG portal URL
- Your organization’s AD FS 2.0
Federation Service name
- Partner Federation Service name
- SharePoint AAM URL (if applicable)
- External URL of external URL-aware
applications (if applicable)
- Alternate publishing name (APN) URLs (if
applicable)
 Note:
Note:In all of the topologies, when an end user connects to the published application for the first time, they may experience long delays while the access request is redirected between the relevant servers. On subsequent connection attempts from any end user, the delays are significantly reduced.Additionally, if the end user security token contains a large number of claims, the user may experience delays when signing in while the claims list is processed. - Forefront UAG portal URL
AD FS claims tracing
Forefront UAG adds all claim values to the Forefront UAG trace file, which can be useful when troubleshooting.
 Caution: Caution: |
|---|
| In many organizations, claim values are created directly from Active Directory attributes; therefore, they can contain personally identifiable information (PII). Therefore, the trace file should be treated as though it contains PII, according to your organization requirements. |




