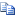
Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) DirectAccess requires end-to-end IPv6 communication between DirectAccess clients and the intranet resources that they connect to. Many resources are not directly accessible over IPv6, including computers that are not capable of running IPv6, or computers with services that are not IPv6-aware (for example, a server that only supports IPv4, or a Windows 2003 server which is IPv6-capable but has services that are not IPv6-aware). When you need to connect to IPv4-only resources on your intranet, you can use the integrated Network Address Translation64 (NAT64) and Domain Name System64 (DNS64) functionality included in Forefront UAG DirectAccess. Both NAT64 and DNS64 are enabled by default in Forefront UAG DirectAccess. NAT64 and DNS64 perform IPv6-to-IPv4 DNS name resolution, and IPv6/IPv4 traffic translation services, for traffic between DirectAccess clients and IPv4-only intranet application servers.
NAT64 and DNS64 provide DirectAccess clients access with access to IPv4-only aware resources by taking takes IPv6 traffic on one side and converting it into IPv4 traffic on the other side. On the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server, NAT64 is used in combination with DNS64. DNS64 intercepts DNS queries and modifies the replies, so that IPv4 address answers to requests for the name of a computer, are converted into the appropriate IPv6 address answers that direct clients to the IPv6 address for the computer on the NAT64. The process is as follows:
- The DirectAccess client sends a DNS name query request to the
Forefront UAG DirectAccess server DNS64 for an address of an
application server. Because DirectAccess clients have only IPv6
connectivity to the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server, the DNS name
query is an IPv6 AAAA request.
- When the DNS64 gets the name query request, it sends two DNS
name queries, an IPv4 query (A) and an IPv6 query (AAAA), to the
corporate DNS configured on the Forefront UAG DirectAccess
server.
- The DNS64 gets a response from the corporate DNS, and decides
which address to return to the DirectAccess client.
The responses can be as follows:
- When the DNS64 receives an IPv6 address (AAAA
record) response from the corporate DNS, the application server has
IPv6 connectivity, and the IPv6 address is returned to the
DirectAccess client.
- When the DNS64 receives an IPv4 address (A
record), the NAT64 acts as a bridge for the traffic. The DNS64
generates an IPv6 address based on the IPv4 address of the
application server, by using the NAT64 prefix configured in the
Prefix Configuration page of the Forefront UAG DirectAccess
Configuration Wizard. The generated IPv6 address is sent to the
DirectAccess client.
- The DNS receives both an IPv6 (AAAA record)
and an IPv4 (A record) address. By default, the DNS64 uses the IPv6
address. In instances where the application server is IPv6 aware
but an application is IPv4-only aware, you can disable the IPv6
interface on the application server, or delete the application
servers IPv6 record from the corporate DNS.
- When the DNS64 receives an IPv6 address (AAAA
record) response from the corporate DNS, the application server has
IPv6 connectivity, and the IPv6 address is returned to the
DirectAccess client.
- The DirectAccess client now has an IPv6 address for the
application server. Traffic is sent directly to the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess server's NAT64, because all IPv6 addresses included in
the NAT64 prefix are automatically routed to the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess server.
- When the NAT64 receives the packet, it extracts from the IPv6
packet the IPv4 address associated with the destination IPv6
address, and transmits the data with an IPv4 header to the
application server.
- The application server sends IPv4 packets to the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess server, which continues the process, as described
above.