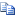
The connection process from DirectAccess clients via the DirectAccess server to the internal network happens automatically, as follows:
- The DirectAccess client computer running Windows 7 Enterprise
or Windows 7 Ultimate, detects that it is connected to a
network.
- When a DirectAccess client starts up or experiences a
significant network change event (such as a change in link status
or a new IP address), it assumes that it is not on the intranet,
and attempts to connect over HTTPS to an intranet Web site (the
network location server) configured during the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess configuration. The client authenticates the server
certificate presented by the HTTPS site, including accessing the
CRL location defined in the server certificate, to verify that the
certificate has not been revoked. If the Web site is available, the
DirectAccess client determines that it is already connected to the
intranet, and the DirectAccess connection process stops. If the Web
site is not available, the DirectAccess client determines that it
is connected to the Internet and the DirectAccess connection
process continues. The name of network location server cannot be
resolved from Internet DNS servers.
- DirectAccess clients located on the Intranet use the name
resolution policy table (NRPT) to determine how to resolve name
requests.
- The DirectAccess client computer connects to the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess server using IPv6 and IPsec. If a native IPv6 network
isn’t available (which is most probable when the user is connected
to the Internet), the client establishes an IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel
using 6to4 or Teredo. The user does not need to be logged in to
complete this step.
- If a firewall or proxy server prevents the client computer
using 6to4 or Teredo from connecting to the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess server, the client automatically attempts to connect
using the IP-HTTPS protocol, which uses a Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL) connection to ensure connectivity.
- As part of establishing the IPsec session, the DirectAccess
client and server authenticate each other using computer
certificates for authentication.
- By validating Active Directory® group memberships, the
Forefront UAG DirectAccess server verifies that the computer and
user are authorized to connect using Forefront UAG
DirectAccess.
 Note:
Note:To mitigate the risk of denial of service (DoS) attacks, IPsec on the Forefront UAG DirectAccess server deprioritizes key negotiation traffic using Differentiated Services Code Points (DSCPs). - If Network Access Protection (NAP) is enabled and configured
for health validation, the DirectAccess client obtains a health
certificate from a Health Registration Authority (HRA) located on
the Internet before connecting to the Forefront UAG DirectAccess
server, or on the intranet using the infrastructure tunnel to the
Forefront UAG DirectAccess server. The HRA forwards the
DirectAccess client’s health status information to a NAP health
policy server. The NAP health policy server processes the policies
defined within the Network Policy Server (NPS), and determines if
the client is compliant with system health requirements; if so, the
HRA obtains a health certificate for the DirectAccess client. When
the DirectAccess client connects to the Forefront UAG DirectAccess
server, it submits its health certificate for authentication. For
more information, see Using Network Access
Protection (NAP) with ForefrontUAG DirectAccess.
- The Forefront UAG DirectAccess server begins forwarding traffic
from the DirectAccess client to the intranet.