Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) does not provide an automated migration from Intelligent Application Gateway (IAG) 2007. Instead, you can manually recreate an IAG 2007 configuration in Forefront UAG. This guide helps you to understand the differences between IAG 2007 SP2 and Forefront UAG, provides guidance about collecting IAG 2007 settings, and information about recreating your IAG configuration in Forefront UAG. We recommend that you review all of the following sections in this document before beginning a migration:
- Summary of differences between IAG
2007 and Forefront UAG—Provides information about
infrastructure differences, a feature comparison, and migration
limitations.
- Collecting IAG 2007
settings—Provides guidance about collecting IAG settings that
you want to recreate in your Forefront UAG deployment.
- Deploying Forefront
UAG—Provides an overview of the main Forefront UAG deployment
scenarios
Summary of differences between IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG
The section provides information about differences in infrastructure, technical features, and migration limitations.
Infrastructure differences
The main differences between IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG are the form factors, and operating system requirements. IAG 2007 is available as a hardware appliance, and in addition IAG 2007 with SP2 is available as a virtual machine. The IAG appliance runs on a 32-bit computer running Windows Server 2003. The IAG 2007 SP2 virtual machine runs on a 64-bit edition of Windows Server 2008, and requires Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V. For more information, see IAG Service Pack 2 system requirements. Forefront UAG is available as a software installation and a hardware appliance. Forefront UAG requirements are summarized in the following table.
|
Processor |
64-bit, 2.66 gigahertz (GHz) or faster processor. Dual core CPU |
|
Memory |
4 GB |
|
Hard drive |
2.5 gigabyte (GB) free space (in addition to Windows requirements) One local hard disk partition that is formatted with the NTFS file system. |
|
Network adapters |
Two network adapters that are compatible with the Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system. These network adapters are used for communication with the internal corporate network, and the external network (Internet). Note that deploying Forefront UAG with a single network adapter is not supported. |
For more detailed information, see System requirements for Forefront UAG servers.
Feature comparison
The following table summarizes feature differences between IAG 2007 SP2 and Forefront UAG.
| Feature/scenario | Supported in Forefront UAG | Supported in IAG 2007 SP2 | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Software installation |
Yes |
No |
IAG 2007 with SP2 can be obtained as a preinstalled hardware appliance or a virtual machine. |
|
Prepackaged VHD (virtual machine) |
No |
Yes |
Forefront UAG can be obtained as a hardware application, or installed as a software application. |
|
Hardware appliance |
Yes |
Yes |
Both IAG 2007 with SP2 and Forefront UAG are available as hardware appliances. |
|
ActivePerl installation |
No |
Yes |
ActivePerl was required for installing and running IAG 2007. It is not required in Forefront UAG. For a list of features installed during Forefront UAG setup, see Verifying installation settings. |
|
Firewall |
Yes |
Yes |
IAG 2007 installs ISA Server 2006 as a firewall. Forefront UAG installs Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG). In both instances, the role of the firewall is to protect the local IAG 2007 or Forefront UAG server. |
|
High availability |
Yes |
Yes (legacy high availability) |
Forefront UAG provides high availability based on Forefront TMG, with the deployment of multiple servers in an array configuration that can be load balanced using Windows NLB, or with hardware load balancers. The Resonate load balancer in IAG 2007 is not available in Forefront UAG. |
|
DirectAccess |
Yes |
No |
Forefront UAG can be deployed as a DirectAccess server, providing seamless access to internal resources for remote clients. For more information see Forefront UAG DirectAccess technical overview. |
|
Client endpoint components |
Yes |
Yes |
There are a number of differences in endpoint requirements between Forefront UAG and IAG 2007. Compare requirements using IAG client endpoint system requirements, and System requirements for Forefront UAG client devices. |
|
Webmail and Basic trunks |
No |
Yes |
Forefront UAG provides only a portal trunk. Webmail and Basic trunks used in IAG 2007 are not available in Forefront UAG. |
|
Web portal for remote access to internal applications |
Yes |
Yes |
Both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG provide a Web portal that allows remote endpoint devices to connect to internal applications published via the portal. In Forefront UAG, the default portal was redesigned to enhance the client endpoint experience. The portal provides an application tree for easier navigation, and the ability to search and sort applications published in the portal. |
|
Web portal with Outlook Web Access look and feel |
Yes |
No |
Forefront UAG provides a streamlined logon experience for Outlook Web Access users. You can apply an Outlook Web Access theme to a portal, and to authentication logon and logoff pages. |
|
Web publishing |
Yes |
Yes |
Both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG allow you to publish Web applications. Forefront UAG does not provide a number of predefined application templates that were provided in IAG 2007, including:
|
|
Browser-embedded applications |
Yes |
Yes |
Both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG allow you to publish browser-embedded applications. Forefront UAG does not provide a number of predefined application templates that were provided in IAG 2007, including:
|
|
Publishing Exchange services with dedicated wizard |
Yes |
No |
Forefront UAG provides a dedicated wizard for publishing Exchange services. Using the wizard, you can publish Microsoft Office Outlook Web Access, Exchange ActiveSync®, and Outlook Anywhere (RPC over HTTP) in a single portal, providing secure access to Exchange services on a single IP address. |
|
Publishing Exchange 2010; SharePoint 2010 |
Yes |
No |
In addition to SharePoint and Exchange 2003 and 2007, you can publish Exchange 2010 and SharePoint 2010 using Forefront UAG. |
|
Publishing Outlook Mobile Access for Exchange 2003 |
No |
Yes |
Publishing this application is not supported in Forefront UAG. |
|
Remote network access with Network Connector |
Yes |
Yes |
In both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG you can provide full VPN access to internal networks using the in-built Network Connector. Forefront UAG adds Network Connector support for 64-bit Windows XP and Windows Vista clients. |
|
Remote network access with SSTP |
Yes |
No |
In addition to the legacy Network Connector application used for Windows XP and Windows Vista endpoints, Forefront UAG provides support for Windows 7 endpoint devices connecting to the internal network over SSTP. |
|
Publishing Remote Desktop Services (RDS) |
Yes |
No |
In addition to the Terminal Services applications you can publish in IAG 2007, using Forefront UAG you can publish Remote Desktop Services (RDS) to provide access to published RemoteApps and Remote Desktops. Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) is integrated in Forefront UAG to provide access to for RDS services and applications. |
|
Publishing a farm of Web servers or application servers |
Yes |
No |
In addition to publishing a single server, using Forefront UAG you can publish a farm of Web servers or application servers that perform the same role or host the same content. Forefront UAG load balances requests to farm members to distribute requests evenly among available nodes, detect offline servers and implement failover, and maintain farm servers without disrupting current endpoint connections. |
|
Client authentication with Active Directory |
Yes |
Yes |
Both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG provide a number of authentication mechanisms including Active Directory. The IAG limit of two domain controllers when configuring Active Directory user authentication was removed in Forefront UAG. |
|
Internal publishing using integrated Windows authentication |
No |
Yes |
Unlike IAG 2007, using Integrated Windows Authentication to authenticate corporate users accessing internal applications is not supported in Forefront UAG. |
|
In-built access policies to verifying the health of endpoint devices |
Yes |
Yes |
In-built policies can be used in both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG. |
|
Network Access Protection (NAP) policies to verify the health of endpoint devices |
No |
Yes |
In addition to evaluating client endpoint health using Forefront UAG endpoint policies, Forefront UAG integrates Windows Server 2008 NAP technology, allowing you to verify client endpoint compliance against NAP policies defined on a Network Protection Server (NPS). For more information, see Planning for endpoint health checking. |
|
Rule set enforcement |
Yes |
Yes |
Rule set enforcement is available in both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG. Rule set enforcement levels were removed in Forefront UAG. |
|
User-defined UniqueIdentifier global host address translation parameter |
No |
Yes |
IAG 2007 uses URL signing to enable communication with multiple internal published servers while using a single external IP address and portal. IAG recognizes the internal server required in an endpoint request by means of a unique host address translation (HAT) URL prefix. The Unique identifier, which is part of this HAT translation prefix is configurable in IAG 2007, but not in Forefront UAG. |
|
Web portal customization |
Yes |
Yes |
You can customize portal settings in IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG. In Forefront UAG portal is now in ASP.Net, not .ASP. |
|
Application wrapper (AppWrap) files |
Yes |
Yes |
AppWrap files enable the manipulation of HTTP requests and responses between backend Web servers and clients. In IAG 2007, there were approximately 30 AppWrap configuration files. Each one was used by a different type of trunk, Basic and Webmail trunks are not used in Forefront UAG, and thus only two AppWrap files exist. One for HTTP trunks, and the other for HTTPS trunks. |
|
Logging to SQL Server |
Yes |
No |
Forefront UAG allows you to log to a local or remote SQL Server. For more information, see Logging to a SQL Server. |
|
Integration of IAG SP2 Update 1 |
Partial |
Yes |
The following features introduced in IAG SP2 Update 1 are included in Forefront UAG RTM:
Other Update 1 issues are not included in Forefront UAG RTM. For more information about Update 1, see Description of Update 1 for IAG Service Pack 2. |
|
Integration of IAG SP2 Update 2 |
Partial |
Yes |
The following features introduced in IAG SP2 Update 2 are included in Forefront UAG RTM:
Other Update 2 fixes are not included in Forefront UAG RTM. For more information about Update 2, see Description of Update 2 for IAG Service Pack 2. |
Migration limitations
This section summarizes IAG 2007 features and settings that cannot be migrated to Forefront UAG, either because the feature has been removed, or because the feature is implemented differently.
The following tools are no longer available in Forefront UAG:
- Service Policy Manager
- User Manager (UserMgrUtil)
- Session Manager (SessionMgrUtil)— IAG 2007
provided the Session Manager Utility
The following limitations apply:
- Configuring Forefront UAG as a domain controller is not
supported.
- Forefront UAG trunks are limited to listening on ports 80 and
443 only. This is a very important consideration when migrating
trunks that use a different port on IAG 2007.
- IAG 2007 Webmail trunks and Basic trunks are no longer
available in Forefront UAG. In Forefront UAG you must use portal
trunks.
- Additional websites cannot be configured in the local IIS
running on the Forefront UAG server. Additional configured websites
for IIS running on the IAG 2007 server cannot be migrated to IIS
running on Forefront UAG.
- Log in to the Forefront UAG management console is not required.
Authentication for Forefront UAG is based on Windows login.
- Integrated Windows authentication is not supported in Forefront
UAG. In Forefront UAG, you must recreate trunks that used this
authentication method in IAG 2007 SP2 to use an alternative form of
authentication.
- ISA Server 2006 was installed automatically on the IAG server.
For Forefront UAG Forefront TMG is installed instead of ISA Server.
Direct configuration of Forefront TMG is not supported (with the
exception of specific settings described in Support boundaries),
and might lead to unexpected behavior if attempted. This includes
(but is not limited to) direct configuration of:
- ActiveSync (published by Forefront UAG now)
- RPC over HTTP (published by Forefront UAG now)
- Custom firewall rules
- Custom publishing settings
- ActiveSync (published by Forefront UAG now)
- Forefront UAG introduces a new trace mechanism that is based on
Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). ETW tracing can now be run on the
both the Forefront UAG server, and on client endpoint devices
connecting to Forefront UAG resources. Files required for
converting Forefront UAG binary traces to readable text are
available from Forefront UAG Tracing Symbols, at the
Microsoft Download Center.
- Running third-party Load Balancing software, such as Resonate
used in IAG, on the Forefront UAG server is not supported.
Forefront UAG provides integrated Windows NLB to balance traffic
for an array of up to eight servers. Alternatively you can use
hardware load balancing products placed in front of the Forefront
UAG servers.
- Some features provided by IAG SP2 updates are not included in
Forefront UAG RTM. Feature that are included are described in the
table in Feature comparison.
Collecting IAG 2007 settings
This section provides information about gathering IAG 2007 settings in preparation for your migration to Forefront UAG. Gather the information in the form of a report that records all the IAG 2007 settings required when configuring Forefront UAG. You can skip this report if the IAG 2007 server is available in parallel when configuring the Forefront UAG server.
Collecting networking information
Collect IAG 2007 network configuration information that is required on Forefront UAG server. These settings include:
- Domain membership details if applicable.
- IP addresses of network adapters
- Subnet masks
- Default gateway information
- Routing table entries
Where?
Collect network information from the IAG server by clicking Network Configuration in the Admin menu of the IAG Configuration console, and from the operating system properties.
Collecting array information
You can gather multiple Forefront UAG servers into an array, where each array member shares the same configuration including trunk and application settings. The legacy IAG 2007 high availability array structure is not supported in Forefront UAG, and a software load balancer cannot be run on the Forefront UAG server. We recommend that you migrate your IAG 2007 array configuration as follows:
- If IAG 2007 high availability array members
share the same configuration, manually recreate the array
configuration settings on a single Forefront UAG server. This
server can then be configured as the Forefront UAG array manager.
When you join other Forefront UAG servers to the array by
connecting them to the array manager, they automatically receive
the configuration and form an array.
- If IAG 2007 high availability array computers
do not share the same configuration, you can do either of the
following:
- Migrate the configuration settings of each IAG 2007 server to a
separate Forefront UAG server. The result is a group of standalone
Forefront UAG servers that each have a different configuration, and
are not part of an array.
- Select a single common configuration for all the IAG 2007 array
servers, and manually recreate this configuration on a Forefront
UAG server. Then create a new array by configuring this server as
the Forefront UAG array manager, and joining other Forefront UAG
servers to it to form an array. Note that each Forefront UAG array
member will have the same configuration as the array manager.
- Migrate the configuration settings of each IAG 2007 server to a
separate Forefront UAG server. The result is a group of standalone
Forefront UAG servers that each have a different configuration, and
are not part of an array.
Collecting client endpoint settings
In order for client endpoint devices to access some internal resources, both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG install client components on connecting devices. In both IAG 2007 and Forefront UAG components are installed using the same methods—online mode; using the Client Components installer; or offline administrator installation. Although there are no changes in endpoint deployment methods, there are a number of changes in client endpoint requirements, including application and browser support. Ensure that you understand the impact of these changes before migrating from IAG to Forefront UAG. For a list of Forefront UAG features that require client components, see Introduction to endpoint component deployment design. For a comparison of requirements, see IAG client endpoint system requirements, and System requirements for Forefront UAG client devices.
Collecting trunk settings
Collect the settings for each trunk currently configured in IAG 2007.
Where?
In IAG 2007 collect the trunk properties as follows:
- Click the IAG console tree, click the HTTP or
HTTPS trunk.
- Note the settings on all property pages and
tabs. For more information about the settings, see Managing IAG portals and published
applications.
Collecting trunk application settings
For each trunk, collect information about the applications published via the trunk.
Where?
In IAG console tree, click the HTTP or HTTPS trunk.
- In the Applications list, select the
application, and then click Edit.
- Note the application settings on all tabs.
For more information about the settings, see Configuring the
properties of applications published by IAG.
Collecting application settings for remote network access
IAG 2007 provides full remote access to the internal network with Network Connector. Forefront UAG also provides Network Connector support, with the addition of Network Connector access support for endpoint devices running 64-bit client operating systems. Collect Network Connector information.
Where?
In IAG 2007 collect the Network Connector information as follows:
- On the Admin menu, click Network Connector
Server.
- On the Network Segment tab, collect network adapter
settings.
- On the IP Provisioning tab, note the static address pool
range of IP addresses assigned to remote clients connecting with
Network Connector.
- On the Access Control tab, collect information about how
VPN clients connected with Network Connector access the Internet.
Note whether clients have Internet access, and whether requests are
routed through the client's original Internet connection, or
through the IAG 2007 server.
- On the Additional networks tab, note the additional
network destinations that are available to VPN clients connecting
with Network Connector. This is applicable if your internal network
has multiple subnets, and you want to allow VPN client access those
subnets.
Collecting trunk certificate information
Collect certificate information.
Where?
- You recorded the names of the server certificates used for each
HTTPS trunk when you noted the settings on the General tab
of each trunk,
- If you want to reuse the IAG 2007 certificates, and the
certificates were created with the option to export the private
key, run the Certificates MMC on the IAG server, and export the
certificates to a location that will be accessible from the
Forefront UAG server.
- If you are using the Certified Endpoints feature on IAG 2007
and have deployed a certification authority (CA) on the IAG server,
note details of the CA configuration so that you can recreate it on
the Forefront UAG server, or on an alternate server.
Collecting authentication server settings
Collect information for each authentication server configured in IAG 2007.
Where?
- Collect authentication server settings—Note the
properties for each authentication server. To do this, on the
Admin menu, click Authentication and User/Group
Servers. Select the required authentication server in the list,
and then click Add.
Note the setting for each authentication server.
- Collect trunk authentication and authorization
settings—Ensure that you recorded the authentication servers
used for session authentication and authorized access to portal
applications. To access authentication server properties in IAG
2007, for each trunk, click the Authentication tab, and note
the listed servers.
- Collect application single sign-on authentication
settings—Note information about the authentication servers used
to authenticate session credentials that are forwarded to backend
published servers. These servers are listed on the Web
Settings tab in the properties of each published
application
Collecting customization settings
This can be very complex as there are many possible customizations that can be applied to IAG 2007. This section provides information only about collecting settings that are fully documented in the Customizing Forefront UAG (other customizations might be possible but are outside the scope of this guide).
Where?
Collect application-specific customizations as follows:
- Custom authentication settings—Stored in the
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\InternalSite\inc\CustomUpdate folder.
- FormLogin customizations—Stored in the
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\Conf\WizardDefaults\FormLogin\CustomUpdate\FormLogin.xml
file.
- AppWrap and SRA customizations—Stored in
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\Conf\Websites\<Trunk_Name>\Conf\CustomUpdate\WhlFiltAppWrap_HTTP.xml
for HTTP trunks. For HTTPS trunks, information is stored in the
WhlFiltAppWrap_HTTPS.xml file in the same location.
- Custom Application templates (for example,
SSLVPNTemplates.xml and WizardDefaultParam.ini)—Stored in the
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\Conf \CustomUpdate folder, or in the
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\Conf\WizardDefaults\CustomUpdate folder.
- File Access shares specific customization
(for example, ShareAccessCfg.xml)—Stored in the
\Whale-Com\e-Gap\von\FileAccess folder.
Collect InternalSite customizations as follows:
- Image files
- INC files
- CSS files
- ASP, HTML files
- Languages XML files
Files are located in CustomUpdate folders, located in subfolders in the \Whale-Com\e-Gap \von\InternalSite folder. For example InternalSite\Images\CustomUpdate.
Collect portal customizations as follows:
- Image files
- INC files
- CSS files
- ASP, HTML files
- Languages XML files
Files are located in CustomUpdate folders, located in subfolders in the \Whale-Com\e-Gap \von\InternalSite folder. For example InternalSite\Images\CustomUpdate.
Deploying Forefront UAG
This section provides information to help you to design and implement your Forefront UAG deployment, including:
- Selecting a network topology
- Installing Forefront UAG
- Configuring Forefront UAG
deployment scenarios
Selecting a network topology
Topology options you need to consider when deploying Forefront UAG include:
- Deployment scope—Consider your fault
tolerance and failover requirements. You can deploy a single
Forefront UAG server, or an array of multiple Forefront UAG servers
that share the same configuration. For more information, see
Identifying your
array deployment goals.
- Network requirements for Forefront UAG
application publishing, and Forefront UAG DirectAccess—You can use
Forefront UAG to publish internal applications via Forefront UAG
trunks, and in addition you can set up the Forefront UAG server to
act as a DirectAccess server. For more information about
infrastructure requirements when setting up Forefront UAG as a
publishing server, see the Infrastructure planning
guide. For information about Forefront UAG DirectAccess
topology requirements, see Forefront UAG
DirectAccess prerequisites.
- Network location—Decide where you want to
place the Forefront UAG server. For example, will it be placed
behind a firewall? For considerations, see the section Networking
and routing requirements in Identifying your
infrastructure deployment goals.
- Domain and workgroup requirements—Forefront
UAG can be deployed as a domain member or in workgroup mode. Domain
deployment is required for the following scenarios:
- Deploy the server as part of a Forefront UAG
array.
- Deploy Forefront UAG as a DirectAccess
server.
- Publish the Forefront UAG File Access
application via a Forefront UAG trunk
- Provide full VPN access to the internal
network by publishing SSTP via a Forefront UAG portal.
- Forward trunk session credentials to backend
published servers using Kerberos constrained delegation.
- Deploy the server as part of a Forefront UAG
array.
- Network adapter and IP address
requirements—There are a number of requirements depending on your
deployment scenarios. For more information, see the section Network
topology requirements in Identifying your
infrastructure deployment goals.
- DNS requirements—There are specific DNS
requirements for Forefront UAG publishing, and Forefront UAG
DirectAccess. For more information, see the section DNS
requirements in Identifying your
infrastructure deployment goals, and Forefront UAG
DirectAccess prerequisites.
Installing Forefront UAG
Ensure that the computers on which you want to install Forefront UAG meet the hardware and software requirements, and that network adapters are installed and configured as required. For more information, see System requirements for Forefront UAG servers. Windows Server 2008 R2 (Standard or Enterprise Edition) should be installed on each computer. Install and initially configure Forefront UAG as follows:
- Join the Forefront UAG computer to a domain (if required)
before installing Forefront UAG.
- Configure network adapters, and routing table entries in the
operating system properties.
- Install Forefront UAG as a software application according to
the instructions in Installing the Forefront
UAG application.
- The first time you open the Forefront UAG Management console,
the Getting Started Wizard runs automatically. Use the wizard to
associate network adapters with internal and external networks, and
to configure Microsoft Update settings. After running the Getting
Started Wizard, you can set up the Forefront UAG computer as a
DirectAccess server if required, and configure the Forefront UAG
server to publish internal applications for remote access.
Configuring Forefront UAG deployment scenarios
You can configure Forefront UAG in a number of deployment scenarios. Some scenarios were available in IAG 2007. Others are new to Forefront UAG. Scenarios include:
- Deploying an
array
- Deploying
DirectAccess
- Deploying
application publishing
- Customizing
Forefront UAG
Deploying an array
Forefront UAG provides a central point of configuration, high availability, and failover with an array feature that allows you to group multiple servers into an array that shares the same configuration. You can optionally load balance traffic to that array. Deploying an array consists of the following steps:
- If you have multiple IAG 2007 servers, decide
how you want to recreate the configuration in Forefront UAG, as
described in Collecting array
settings.
- Read background information about planning an
array deployment in the Array planning
guide.
- After recreating the IAG configuration on a
Forefront UAG server, configure that server as the array manager,
as described in Configuring the array
manager server.
- Join each server that will be part of the
array to the array manager server, as described in Joining a server to an
array.
- Load balance traffic to the array as
described in Configuring NLB for a
Forefront UAG array.
Deploying DirectAccess
In addition to publishing internal applications via trunks, Forefront UAG can be deployed as a DirectAccess server. For more information, see:
- Understand more about DirectAccess using the
Forefront UAG
DirectAccess technical overview.
- Prepare your network infrastructure for a
DirectAccess deployment, as described in Planning a Forefront UAG
DirectAccess deployment strategy.
- Ensure your deployment meets requirements, as
described in Forefront UAG
DirectAccess prerequisites.
- Deploy Forefront UAG DirectAccess as
described in the Forefront UAG
DirectAccess deployment guide.
Note that you cannot publish Network Connector when DirectAccess is deployed.
Deploying application publishing
Forefront UAG implements application publishing via trunks, similar to the architecture used in IAG 2007. Recreate your IAG 2007 publishing configuration using the guidelines described in the following topics.
Deploying certificates for publishing
Like IAG 2007, Forefront UAG application publishing might require certificates installed on the Forefront UAG server as follows:
- HTTPS trunks—If you want to create HTTPS
trunks in Forefront UAG, you need server certificates located on
the Forefront UAG server, to authenticate the server to endpoint
client devices connecting over an HTTPS connection. If you exported
the certificates used in IAG, then import the certificates to the
Personal Store on the Forefront UAG server, and then select the
appropriate certificate when you set up an HTTP trunk.
- Certified endpoints—If you deployed the
certified endpoint feature in IAG 2007, and issued the certificates
from a CA running on the IAG server, you will need to recreate the
CA that issues endpoint certificates on the Forefront UAG server or
on a remote server, in order to continue to use the certified
endpoint feature.
For information about certificate requirements, see Mapping your deployment goals to an infrastructure design.
Deploying authentication servers for publishing
Similarly to IAG 2007, in Forefront UAG you use authentication servers to authenticate and control client endpoints accessing Forefront UAG resources. Forefront UAG supports the same authentication methods as IAG 2007, with the exception of Integrated Windows Authentication which is not supported in Forefront UAG. Deploy authentication servers for publishing as follows:
- Set up authentication servers as required. You can skip this
step if you are continuing to use the same authentication servers
that you used for IAG 2007.
- Predefine authentication servers in Forefront UAG on the
Authentication and Authorization Servers tab on the
Admin menu. Each server you predefine on this tab is used as
it was in IAG 2007:
- When you create a new trunk, you can select
servers to authenticate client sessions to Forefront UAG
portals.
- When you publish an application in a portal,
you can select servers to authenticate session credentials that are
forwarded to backend published servers
- When you configure authorization to specify
who can access specific portal applications, you can use user
accounts and groups configured on authentication servers to control
authorized access.
- When you create a new trunk, you can select
servers to authenticate client sessions to Forefront UAG
portals.
- For each trunk you create, on the Authentication page of
the Create Trunk Wizard, specify an authentications server against
which session credentials are verified. For more information, see
Setting up a
trunk.
- For each application you publish in the trunk, do the
following:
- On the Authentication page of the Add Application
Wizard, specify the authentication server against which credentials
forwarded to backend published servers should be verified. For more
information, see Adding applications to a
trunk.
- After adding an application to the trunk using the Add
Application Wizard, select the application on the main page of the
trunk properties, and click Edit. On the
Authorization page of the application properties, optionally
specify user and group accounts that have access to a specific
application.
- On the Authentication page of the Add Application
Wizard, specify the authentication server against which credentials
forwarded to backend published servers should be verified. For more
information, see Adding applications to a
trunk.
Deploying access policies
Forefront UAG can verify the settings of client endpoints devices using in-built access policies similar to those in IAG 2007. Like IAG 2007, you can select in-built policies when creating a trunk with the Create Trunk Wizard. You can also modify in-built policies, and create custom access policies. See Configuring Forefront UAG access policies for more information. Forefront UAG also provides a new feature that checks the health of endpoint devices against Network Access Protection (NAP) policies downloaded from a Network Policy Server (NPS For more information, see Configuring NAP access policies.
Creating trunks
Like IAG 2007, Forefront UAG uses trunks to represent a combination of IP address and port via which internal applications are published. You create a trunk and then publish applications via the trunk, as follows:
- For each IAG portal trunk, create an HTTP or
HTTPS portal trunk with the same configuration in Forefront UAG,
using the Create Trunk Wizard. For more information, see Implementing a
trunk.
- In Forefront UAG Basic and Webmail trunks are
not supported. For each IAG Basic or Webmail trunk, create an HTTPS
or HTTPS portal trunk in Forefront UAG using the Create Trunk
Wizard. If you want to allow remote users to access the application
directly and not through the portal, do the following:
- When publishing SharePoint 2007 or SharePoint
2010, you can provide access directly to the SharePoint application
using alternate access mappings. For more information, see the
SharePoint
publishing solution guide.
- When publishing other Web applications, add
the applications to the wizard by selecting the Other Web
Application (application specific hostname) option in the Add
Application Wizard. For more information, see What happened to Webmail and Basic
trunks?, on the Forefront UAG product team blog.
- When publishing SharePoint 2007 or SharePoint
2010, you can provide access directly to the SharePoint application
using alternate access mappings. For more information, see the
SharePoint
publishing solution guide.
Note the following:
- In Forefront UAG there is an ADFS trunk. This
is used when you set up a trunk with ADFS 1.0. For more
information, see the Active Directory
Federation Services 1.x solution guide.
- In Forefront UAG duplicating trunks is not
supported. You must create each trunk separately.
Publishing applications via a trunk
As described in Feature comparison, Forefront UAG no longer provides many of the application-specific templates that were provided in IAG 2007. Instead, you should use one of the following for publishing applications that do not have a specific template:
- Other Web Application (application specific
hostname)—Use this option to publish a Web application that does
not appear on the application list in the Add Application Wizard.
This option allows endpoint devices to access this application
directly as well as via the portal. To connect directly, users type
in the application host name instead of the portal host name.
- Other Web Application (portal specific
hostname)—Use this option to publish a Web application that does
not appear on the application list in the Add Application
Wizard.
- Generic Browser-Embedded App (Multi
Servers)—Use this option to publish a browser-embedded application
that does not appear on the applications list in the Add
Application Wizard.
- Generic non-Web applications—In the non-Web
application category of the Add Application Wizard, there are a
number of generic applications that you can select.
For more information, see Adding applications to a trunk, and Configuring application settings.
Note that in addition to publishing a single Web server, using Forefront UAG you can publish a farm of Web servers or application servers that perform the same role or host the same content. Requests to farm members are load balanced to distribute requests evenly among available nodes, detect offline servers and implement failover, and maintain farm servers without disrupting current endpoint connections. For more information, see Planning for application and server farm publishing.
Publishing Exchange
Forefront UAG provides a dedicated wizard for publishing multiple Exchange services. Using the wizard, you can publish Microsoft Office Outlook® Web Access, Exchange ActiveSync®, and Outlook Anywhere (RPC over HTTP) in a single portal, providing secure access to Exchange services on a single IP address. Forefront UAG also supports publishing of Exchange 2010.
After collecting publishing settings for Exchange 2003/2007 publishing (ActiveSync, OWA) in IAG 2007, set up a portal trunk that publishes all Exchange applications as a single trunk. For more information, see the Exchange services publishing solution guide. By default the trunk is configured to apply an Outlook Web Access theme to a portal, providing an easily recognizable experience for Outlook Web Access users. Authentication logon and logoff pages also have an Outlook Web Access look and feel.
Publishing SharePoint
Like IAG 2007, you can publish SharePoint in Forefront UAG. In addition to SharePoint Portal Server 2003 and SharePoint 2007 that you can publish with IAG, Forefront UAG also provides support for publishing SharePoint Server 2010.
After collecting SharePoint 2003 and 2007 application information from IAG 2007, publish SharePoint in Forefront UAG using the SharePoint publishing solution guide.
Publishing full remote access to internal networks
Like IAG 2007, in Forefront UAG you can provide full remote access to internal networks using the in-built Network Connector. Copy the IAG configuration settings over to Forefront UAG, using the SSL Network Tunneling page in Remote Network Access on the Admin menu. After configuring the settings, you can publish the Remote Network Access application(Network Connector) in a trunk. For more information, see Publishing remote network access with Network Connector. Note that Network Connector is not available for client endpoints running Windows 7. To provide full remote access for these clients you must publish SSTP. In addition, you cannot publish Network Connector if Forefront UAG is acting as a DirectAccess server.
In addition to Network Connector, using Forefront UAG you can provide full access to internal networks using SSTP. Note that SSTP access is only available to clients running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2. Clients can only access SSTP via the Forefront UAG portal. Connecting to SSTP directly via a dial-up connection is not supported. For more information, see Publishing remote network access with SSTP.
Publishing Remote Desktop Services (RDS
If you published a Terminal Services Web Client application or Microsoft Windows Xp/Vista Terminal Services application in IAG 2007, you can republish these applications in a Forefront UAG trunk using the TS Web Client Tunneling and the TS Client Tunneling applications. In addition, using Forefront UAG you can publish RemoteApps and Remote Desktops. A Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) is integrated into Forefront UAG to provide an application-level gateway for RDS services and applications. For more information, see theRemote Desktop Services publishing solution guide.
Publishing File Access
As in IAG 2007, in Forefront UAG you can publish the File Access and Local Drive Mapping applications in your portal trunk to allow remote users to access corporate file systems on the internal network. You configure Forefront UAG File Access in the same way as IAG 2007. For more information, see:
- For instructions on providing access to
Windows shared network folders by configuring the Local Drive
Mapping application, see Configuring Local Drive
Mapping.
- For information about configuring the File
Access application to provide access to Windows network servers and
Novell Netware file servers, see Configuring File
Access.
- To configure permissions that specify which
remote users can access mapped drives and file access servers, see
Configuring file
server and share permissions.
- For instructions on publishing the File
Access application in a Forefront UAG portal, see Publishing File Access
and Local Drive Mapping applications
There are a number of File Access limitations in Forefront UAG:
- To allow remote access to Windows file
servers, Forefront UAG must be a domain member. It must belong
either to the domain to which the file servers reside, or must be a
member of a trusted domain.
- Both Forefront UAG and file access servers
must be members of the same domain in which users are located, or
in a trusted domain.
- The File Access application does not support
use of Kerberos constrained delegation (KCD) to provide single
sign-on (SSO) functionality
- There are some issues with Unicode support
when publishing File Access in Forefront UAG.
Configuring event logging and monitoring
Forefront UAG provides the same event logging options as IAG 2007, and you can configure the same log settings. In addition, Forefront UAG allows you to log to a local or remote SQL Server. For more information, see Logging to a SQL Server. Forefront UAG also provides a management pack for monitoring Forefront UAG servers via a System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) server. For more information, see Using System Center Operations Manager (SCOM).
Customizing Forefront UAG
Like IAG 2007, in Forefront UAG you can customize the front-end portal, InternalSite settings, endpoint components, and the Web Monitor application.
Portal customizations
The Forefront UAG portal is an ASP.Net-based Web application using Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (AJAX). Migration of INC files, CSS files, ASP files, HTML files and Languages XML files from IAG 2007 may be complex, depending on the extent of the IAG 2007 customization. With changes in Forefront UAG portal architecture, it might be simpler to redefine portal customizations in Forefront UAG, using IAG 2007 customizations as a guideline. For more information, see Customizing the portal.
InternalSite customizations
Like IAG 2007, Forefront UAG uses an ASP-based Web application, called InternalSite, to provide functionality including authentication services for portal trunks, and installation of client endpoint components. Depending on the extent of InternalSite customizations in IAG 2007, it might be too complex to recreate the exact INC files, CSS files, ASP files, HTML files and languages XML files settings in Forefront UAG. It might be simpler to redefine portal customizations in Forefront UAG, using IAG 2007 customizations as a guideline. For more information, see Customizing the InternalSite.
Endpoint component customizations
Like IAG 2007, there are a number of custom settings you can configure for Forefront UAG endpoint components. Recreate IAG settings in Forefront UAG using the instructions described in Customizing endpoint components.
HTTP response customizations with AppWrap
As in IAG 2007, the Forefront UAG Application Wrapper (AppWrap) configuration files enable the manipulation of HTTP requests and responses between backend Web servers and clients. In IAG 2007, there were approximately 30 AppWrap files. Each one was used by a different type of trunk. In Forefront UAG Basic and Webmail trunks are not used, and thus only two AppWrap files exist—one for HTTP trunks, and the other for HTTPS trunks. The size of these AppWrap files have also been reduced. Note the following changes:
- The Forefront UAG AppWrap structure has changed to support
manipulation per application. Each group of <DATA_CHANGE>
tags is enclosed within
<APPLICATION_TYPE>[APP_TYPE]</APPLICATION_TYPE> tags,
where APP_TYPE represents the application ID defined in the top
part of WizardDefaultParam.ini and then inside []. For example,
[ExchangePub2007]. It is still possible to define an empty
APPLICATION_TYPE as follows:
<APPLICATION_TYPE></APPLICATION_TYPE>, for any other
manipulation for a non-defined application. This change improves
the “search & replace” manipulation mechanism, and thus
enhances performance.
- In order to port custom IAG-style AppWrap files to the
Forefront UAG format, some manual changes of the original file are
needed. After the <MANIPULATION> tag, add a
<MANIPULATION_PER_APPLICATION> tag, immediately followed by
an <APPLICATION_TYPE>[APP_TYPE]</APPLICATION_TYPE> tag.
Ensure you add a closing </MANIPULATION_PER_APPLICATION> tag
after all the <DATA_CHANGE> sections, before the beginning of
the <HEADER_CHANGE> section, as follows:
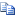 Copy Code
Copy CodeAPP_WRAP ver="3.0" id="RemoteAccess_HTTPS.xml"> <MANIPULATION> <MANIPULATION_PER_APPLICATION> <APPLICATION_TYPE>InternalSite</APPLICATION_TYPE> <DATA_CHANGE> <URL case_sensitive="false">…</URL> <SAR> <SEARCH encoding="base64">…</SEARCH> <REPLACE encoding="base64" using_variables="true">…</REPLACE> </SAR> </DATA_CHANGE> … … … </MANIPULATION_PER_APPLICATION> <HEADER_CHANGE>
- Conditional SAR (search and replace) is a new feature
introduced in Forefront UAG. It enables the AppWrap engine to
perform actions only when certain conditions related to a session
parameter are met.
- After modifying the AppWrap file, save it, and then
double-click the file to open it in Internet Explorer. If it opens
without any errors, this indicates that the XML file syntax is
correct, and thus the file can be used by Forefront UAG.
For more information about AppWrap, see Manipulating HTTP responses with AppWrap.
Web Monitor customizations
Like IAG 2007, you can customize settings for the Web Monitor in Forefront UAG. You can recreate IAG customization settings in Forefront UAG. For instructions, see Customizing the Web Monitor.
For more information about Forefront UAG arrays, see the Array planning guide. For more information, see Managing IAG client endpoint policies, and Planning for endpoint health checking. . For more information, see About publishing applications in an IAG portal, and Introduction to publishing design. For more information, see Publishing Outlook Web Access on a Forefront UAG portal. For more information, see the Customizing Forefront UAG. For more information, see What happened to Web mail and Basic trunks? on the Forefront UAG Product Team Blog. For more information, see the Exchange services publishing solution guide. For more information, see the Exchange services publishing solution guide and the SharePoint publishing solution guide
Shutting down the IAG 2007 server
In a scenario where IAG and 2007 coexist, and a firewall is located between the IAG or Forefront UAG server on one side, and the Internet on the other, do the following to shut down the IAG server:
- Change the IP address— Configure the firewall to pass incoming
connection requests to the new IP address of Forefront UAG instead
of IAG 2007.
- Remove the IAG server from production— Wait for the current
sessions to drain from IAG 2007 and then the shut down the
server.
Note the following:
- If the IAG 2007 server connects directly with a public IP
address, the complexity and restrictions for shutting down the IAG
server will depend on the specific network configuration. The
easiest solution in such a case might be to shut down IAG 2007
before deploying the Forefront UAG server.




